BTR-Cl
CAS Number 2410661-17-3
Materials, Organic Conductors, Semiconducting Molecules, Small Molecule OPV DonorsBTR-Cl, highly crystalline small molecular donor
High purity and available online for fast, secure dispatch
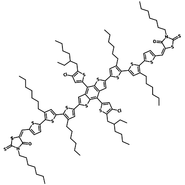
Like its BTR derivative, BTR-Cl (CAS number 2410661-17-3) has a backbone consisting of a benzodithiophene (BDT) unit in conjugation with two terthiophenes and two rhodanine periphera end groups forming a coplanar structure showing nematic liquid crystal behaviour.
BTR-Cl is a highly crystalline small molecular donor with even stronger intermolecular interaction, low-lying molecular energy levels, and a strong tendency for edge-on orientation.
Multi-functional molecule
Nematic liquid crystal behaviour
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Small molecule donor in OPVs
Achieving PCE over 15%
Highly crystalline molecule
Low-lying molecular energy levels.
A record-high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 13.6% for ASM OSCs was achieved using BTR-Cl as electron donor and Y6 as electron acceptor [1]. Later on, 14.7% efficiency of the same donor acceptor BTR-Cl:Y6 system was obtained with a FF of 74.7%, and JSC of 23.66 mA cm-2 at the concentration of 18 mg/ml BTR-Cl:Y6 solution [2]. Further improvement leading to a record PCE of 15.34% was gained when 5 wt% of PC71BM was added in the active layer [3]
Device structure 1: ITO/PEDOT:PSS/BTR-Cl:Y6 (1.6:1)/Phen-NaDPO/Ag
| Thickness (nm) | VOC (V) | JSC (mA cm-2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
| 110 | 0.86 | 24.0 | 64.6 | 13.61 |
Device structure 2: ITO/PEDOT:PSS/BTR-Cl:Y6 (1.6:1)/Phen-NaDPO/Ag
| Thickness (nm) | VOC (V) | JSC (mA cm-2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
| 110 | 0.83 | 23.66 | 74.7 | 14.70 |
Total concentration of the active layer is 18 mg/ml
Device structure 3: ITO/PEDOT:PSS/BTR-Cl:Y6:5 wt% PC71BM (1.8:1:0.1)/Phen-NaDPO/Ag
| Thickness (nm) | VOC (V) | JSC (mA cm-2) | FF (%) | PCE (%) |
| 110 | 0.838 | 23.75 | 77.11 | 15.34 |
General Information
| Full name | 5,5'- [[4,8-bis[5-(2-ethylhexyl)-4-chloro-2-thienyl]benzo[1,2-b:4,5-b']dithiophene-2,6-diyl]bis[(3',3''-dihexyl[2,2':5',2''-terthiophene]-5'',5-diyl)methylidyne ]]bis[3-hexyl-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone] |
| Purity | 98% (1H NMR) |
| Synonyms | BTR-Cl |
| Chemical formula | C102H126Cl2N2O2S14 |
| Molecular weight | 1931.97 g/mol |
| CAS number | 2410661-17-3 |
| HOMO / LUMO | HOMO = -5.46 eV LUMO = -3.70 eV [1] |
| Melting point (DSC) | 226°C, 195°C (Tg) |
| Absorption | λmax 580 nm, 624 nm in film |
| Color/form | Dark purple powder/crystals |
| Solubility/processing solvents | Chloroform, chlorobenzene |
| Classification / Family | Benzodithiophene (BDT) derivatives, Heterocyclic five-membered ring, Organic semiconducting materials, Organic Photovoltaics, Small molecule donor, SM-OPVs, Liquid crystal |
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
Pricing
| Batch | Quantity | Price |
| M2257A1 | 100 mg | £520 |
| M2257A1 | 250 mg | £1050 |
| M2257A1 | 500 mg | £2000 |
| M2257A1 | 1 g | £3500 |
| M2257A1 | 5 - 10 g* | Please enquire |
Literature and Reviews
- All-Small-Molecule Organic Solar Cells with an Ordered Liquid Crystalline Donor, H. Chen et al., Joule 3, 3034–3047 (2019); DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.09.009.
-
Delicate Morphology Control Triggers 14.7% Efficiency All-Small-Molecule Organic Solar Cells, H Tang et al., Adv. Energy Mater., 2001076 (2020); DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202001076.
- 15.34% Efficiency All-Small-Molecule Organic Solar Cells with Improved Fill Factor Enabled by a Fullerene Additive, D. Hu et al., Energy Environ. Sci., 13, 2134-2141 (2020); DOI: 10.1039/D0EE00714E.

 BTR-Cl MSDS sheet
BTR-Cl MSDS sheet