Molybdenum Sulfide Selenide (MoSSe) Powder
CAS Number 132004-88-7
2D Materials, Anode Materials, Battery Materials, Inorganic Electronic Materials, Low Dimensional Materials, Materials,MoSSe Powder, used to prepare nanosheets and nanoparticles through liquid exfoliation
High quality and high purity 2D semiconducting material available for priority dispatch
Technical Data | MSDS | Structure | Literature and Reviews | Related Products | Resources and Support
Molybdenum sulfide selenide (MoSSe), CAS number 132004-88-7, is a two-dimensional TMDC. It is often referred to as a "Janus" MXY transition metal dichalcogenide.
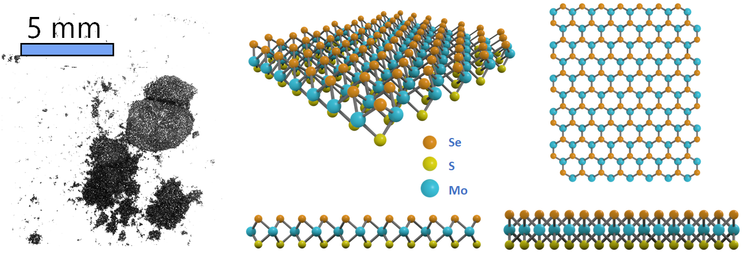
Janus MoSSe consists of three layers of atoms: Sulfur, molybdenum, and selenium from the top to the bottom in the sequence of S-Mo-Se. The geometry of monolayer Janus MoSSe is different from MoS2 and MoSe2 - with one side of the Janus MoSSe structure being S atoms, and the other side being Se atoms. The Mo atom layer is sandwiched between S and Se layers, and multilayers of MoSSe are stacked by the vdW interactions. Due to the the structural asymmetry and a large out-of-plane piezoelectric polarisation of Janus MoSSe, it is possible to stack the dipoles of the individual layers and obtain an atomically-thin pn-junction across the multilayer system by stacking multiple Janus MoSSe layers on top of each other.
High Purity
≥99.995% Molybdenum Sulfide Selenide
Worldwide Shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Low Cost
Low Cost Molybdenum Sulfide Selenide
Liquid Exfoliation
Prepare nanosheets and nanoparticles through liquid exfoliation
Similar to MoS2, the MoSSe monolayer also exhibits a honeycomb pattern from the top view of the lattice. However, the mirror symmetry is broken due to the different electronic properties of sulfur and selenium, which leads to the polar properties of MoSSe.
Technical Data
| CAS Number | 132004-88-7 |
| Chemical Formula | MoSSe |
| Molecular Weight | 206.96 g/mol |
| Bandgap | 2.14 eV (direct) [1] |
| Preparation | Synthetic - Chemical Vapour Transport (CVT) |
| Structure | Hexagonal |
| Electronic Properties | 2D Semiconductor |
| Melting Point | N/A |
| Colour | Black |
| Classification / Family | Janus transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), 2D semiconductor materials, Nano-electronics, Nano-photonics, Materials science |
Product Details
| Form | Purity |
|---|---|
| Powder | ≥99.995% |
Pricing Table
| Product Code | Form | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| M2143C1 | Powder | 500 mg | £220 |
| M2143C1 | Powder | 1 g | £360 |
MSDS Document
 Molybdenum sulfide selenide powder
Molybdenum sulfide selenide powder
Structure of Molybdenum Sulfide Selenide Powder
Literature and Reviews
- Tunable Electronic and Optical Properties of Monolayer and Multilayer Janus MoSSe as a Photocatalyst for Solar Water Splitting: A First-Principles Study, Z. Guan et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 122, 6209−6216 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b00257.
- Distorted Janus Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: Stable Two-Dimensional Materials with Sizable Band Gap and Ultrahigh Carrier Mobility, X. Tang et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 122, 19153−19160 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b04161.
- Efficient Charge Separation in 2D Janus van der Waals Structures with Built-in Electric Fields and Intrinsic p−n Doping, A. C. Riis-Jensen et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 122, 24520−24526 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b05792.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of 2D materials available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.



