Spiro-TTB
CAS Number 515834-67-0
Charge Transport Layer Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Hole Transport Layer Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Perovskite Interface Materials,Spiro-TTB, HTL material in OLED, OPV and perovskite solar cells
Used to improve device performance
Overview | Specifications | Pricing and Options | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
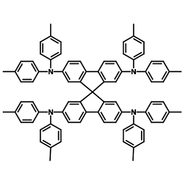
Spiro-TTB has a spirofluorene core with four attached ditolylamine at the 2 and 7 positions of spirofluorene. Like Spiro-OMeTAD, it is electron-rich and commonly used as a hole-transport layer material in OLED, OPV, and perovskite solar cells.
Compared to Spiro-OMeTAD, Spiro-TTB is less electron-rich, with four methoxyl groups being replaced by four methyl groups. It has a deeper HOMO energy level, which gives greater VOC, thus, better device performance can be expected.
General Information
| CAS number | 515834-67-0 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 2,2',7,7'-Tetra(N,N-di-p-tolyl)amino-9,9-spirobifluorene |
| Chemical formula | C81H68N4 |
| Molecular weight | 1097.43 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 384 nm in DCM |
| Fluorescence | λmax 413 nm in DCM |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.25 eV [1] |
| Classification / Family | Spirofluorene derivative, Hole transport layer materials, Perovskite solar cells, Organic electronics. |
Product Details
| Purity | Unsublimed > 98% (1H NMR) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | Tg = 146 °C |
| Appearance | Light yellow powder/crystals |
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO (90 nm)/Spiro-TTB:F6-TCNNQ (4 wt.%, 10 nm)/NPB (20 nm)/NPB:Ir(MDQ)2acac (10 wt.%, 10 nm)/BAlq (65 nm)/BPhen:Cs (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour |
|
| Max. Power Efficiency | 33.3 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 27.7 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 19.5% |
| Device structure | ITO (90 nm)/Spiro-TTB:F6-TCNNQ (4 wt.%, 10 nm)/NPB (20 nm)/TCTA:Ir(ppy)2acac (8 nm)/TPBi:Ir(ppy)2acac (12 nm)/BAlq (50 nm)/BPhen:Cs (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour |
|
| Max. Power Efficiency | 77.0 lm W−1 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 54.4 cd/A |
| Max. EQE | 19.7% |
| Device structure | ITO/NPB (75 nm)MoO3 (2 nm)/Au (2 nm)/Ag (6 nm)/Spiro-TTB:F6-TCNNQ (2 wt.%, 10 nm)/NPB (10 nm)/NPB:Ir(MDQ)2acac (10 wt.%, 20 nm)/BAlq (10 nm)/BPhen:Cs (85 nm)/Ag (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour |
|
| Max. EQE | 39.6% |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited references
Pricing
| Grade | Order Code | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unsublimed (>98% purity) | M2192B1 | 500 mg | $273 |
| Unsublimed (>98% purity) | M2192B1 | 1 g | $455 |
| Unsublimed (>98% purity) | M2192B1 | 5 g | $1,885 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Minimal Effect of the Hole-Transport Material Ionization Potential on the Open-Circuit Voltage of Perovskite Solar Cells, R. Belisle et al., ACS Energy Lett., 1, 556−560 (2016); DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00270.
- Alternative p-doped hole transport material for low operating voltage and high efficiency organic light-emitting diodes, C. Murawski et al, Appl. Phys. Lett. 105, 113303 (2014); doi: 10.1063/1.4896127.
- Coupled Optical Modeling for Optimization of Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with External Outcoupling Structures, M. Kovačič et al., ACS Photonics 2018, 5, 422−430 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00874.


 Spiro-TTB MSDS sheet
Spiro-TTB MSDS sheet