Displacement vs Pressure Controlled Syringe Pump


When selecting a syringe pump for your application, one key factor to consider is the pump's operating principle. Do you need a pressure or displacement syringe pump?
Broadly speaking:
- Displacement syringe pumps control volume of liquid dispensed by controlling the physical displacement the plunger flange. This maintains a constant flow rate.
- Pressure syringe pumps control fluid delivery so that the liquid flows at a consistent pressure. These systems use a feedback loop connected to a pressure sensor to maintain this constant fluid pressure.
What Are Displacement Syringe Pumps?
Displacement syringe pumps, also known as volumetric pumps control the movement of the syringe plunger to deliver a specific volume of fluid over time. The pump's stepper motor or servo motor drives the lead screw, which in turn advances the syringe plunger at a predetermined rate. This direct control over the plunger position allows for highly accurate and reproducible fluid delivery.
Advantanges of displacement syringe pumps include:
- High precision and accuracy in fluid delivery
- Ability to deliver a wide range of flow rates
- Compatibility with a variety of syringe sizes and materials
- Suitability for applications requiring precise volume control
- Easy to set up, use and integrate with existing experimental systems
However, displacement syringe pumps struggle when working with compressible fluids or against high back pressures. This is because the pump does not directly monitor or control the fluid pressure. Another limitation of these systems is that they are not suitable for working with highly pressure-sensitive systems.
Displacement syringe pumps are easy to use and can achieve a wide range of flow rates. Alongside their precise volume dispensing control, these qualities make displacement syringe pumps, such as an Ossila Syringe Pump, suitable for most applications.
What Are Pressure-Controlled Syringe Pumps?
Pressure syringe pumps, also referred to as constant pressure pumps, maintain a constant fluid pressure throughout the delivery process. These pumps use a pressure sensor to monitor the fluid pressure. This pressure sensor feeds into a microcontroller, which delivers signals to the motor driver. This signal will adjust the plunger velocity in order to maintain the desired pressure setpoint. Constant pressure systems ensure that fluid is dispensed at a consistent pressure, regardless of changes in system resistance or fluid properties.
Advantages of pressure syringe pumps include:
- Ability to deliver fluids at a constant pressure
- Improved performance with compressible fluids, extremely viscous solutions or against variable back pressures
- Reduced risk of over-pressurization and sample damage
- Suitability for applications needing precise pressure control
- More adaptable for dispensing solutions with unknown or variable fluid, and will compensate for system and external variabilities.
However, pressure syringe pumps may have a limited flow rate range. They also may require a significant response time to reach the desired pressure setpoint. This will waste material and make dispensing more difficult.
Pressure driven syringe pumps are vital when working with systems that rely on constant pressure, or if you are working with particularly difficult solutions. However, they require more complex control systems than displacement syringe pumps so are often built directly into bigger experimental set ups.
Choosing the Right Syringe Pump For You
The choice between a displacement and pressure syringe pump depends on the specific requirements of your experimental setup.
| Displacement Syringe Pump Applications | Pressure Syringe Pumps Applications |
|---|---|
|
High Precision / Low Volume Dispensing If you require precise control over flow rates and volumes, choose displacement syringe pumps. They are highly accurate and can deliver a wide range of flow rates reliably. The direct control over the plunger position allows for precise metering of small volumes. Examples applications: microfluidic and lab-on-a-chip applications, miniaturized devices and sensitive assays. |
Pressure-Sensitive Applications For experiments involving pressure-sensitive samples or devices, you may require a pressure syringe pump. Maintaining a constant pressure is essential to prevent damage to delicate biological samples. Pressure systems can automatically adjust flow rates, ensuring gentle and consistent fluid delivery. Example applications: cell culture perfusion or microfluidic organ-on-a-chip systems. |
|
Chromatography and Separation Techniques In chromatography and separation techniques, a constant flow rate is critical for reproducible results. Displacement syringe pumps are well-suited for this. They can deliver stable and accurate flow rates over extended periods. Programmable flow rate gradients are also valuable for optimizing separation conditions. Example applications: high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or capillary electrophoresis (CE). |
Viscous or Compressible Fluids For viscous or compressible fluids, pressure syringe pumps provide more consistent and reliable fluid delivery. As the fluid properties change during the experiment, a pressure syringe pump can adapt the flow rate to maintain the desired pressure, ensuring a stable delivery rate. This is particularly important in applications such as polymer processing or gas solubility studies. |
For well known solutions with predictable fluid properties, constant displacement pumps will provide precise and consistent fluid delivery and are more straightforward to use.
There are specific cases where pressure controlled syringe pumps provide value, but for most controlled laboratory applications where precise flow rate is necessary and conditions are stable, a constant displacement pump will generally serve better.
Syringe Pump

Learn More
 How do Syringe Pumps Work?
How do Syringe Pumps Work?
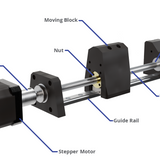
Syringe pumps are electromechanical devices that are designed to convert rotational motion into linear motion.
Read more... How To Set Up and Use The Ossila Syringe Pump
How To Set Up and Use The Ossila Syringe Pump
The Ossila Single Syringe Pump and Ossila Dual Syringe Pump are quick and easy to set up and use. Both models have similar internal circuitry, in-built software, and controls.
Read more...We used pre-trained AI to help us write this page. As part of our editorial process, our in-house experts review, fact-check, and edit all AI-generated content to make sure we provide you with accurate and helpful information.