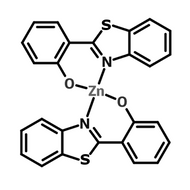
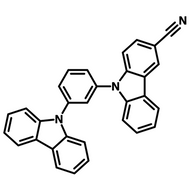
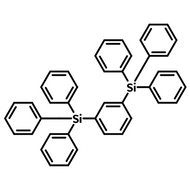
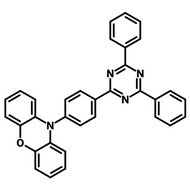
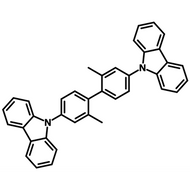
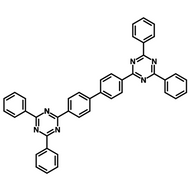
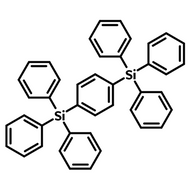
Host Materials
Host materials for fluorescent and phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) and thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) devices. Maximize your device efficiency by fabricating and testing new devices in a glove box environment.
Host materials play a crucial role in the emissive layer in OLEDs. They assist in transporting electrons and holes efficiently and are therefore described as ambipolar. Host materials transfer energy to the light-emitting molecules/dopants and in some cases, a single molecule can serve as both the host and emitter. On top of this they can stabilize the charge carriers to promote longevity as well as efficiency.
Host materials can be placed into three categories:
- Fluorescent Host Materials
- Phosphorescent Host Materials
- TADF Host Materials
Selecting the correct material type depends on selection the specific requirements of the device, such as color, efficiency, and operational stability. Please contact Ossila if you would like some advice.
Jump to: Browse Host Materials by Collection | Browse all Host Materials | Resources and Support
Browse Host Materials by Collection
Browse all Host Materials
Related categories: OLED materials, Transport layer materials, OLED dopant materials, TADF materials
Filter by price change:
Filter by photoluminescence:
Filter by purification technique:
Page 1 of 2
Resources and Support
Fluorescence and phosphorescence are types of photoluminescence. Photoluminescence refers to radiative emissions where the absorbance of a photon is followed by the emission of a lower energy photon. The main empirical difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence is the time in between absorbance and the emission of photons. Fluorescence is where a material absorbs a photon, and almost immediately emits a lower energy photon.
Read more... Organic Light Emitting Diodes
Organic Light Emitting Diodes
Organic light emitting diodes are thin film devices that convert electrical energy into visible light. In OLED devices, electrons and holes are injected into the organic medium and recombine radiatively via electroluminescence (EL). The colour of the light emitted is dependent on the molecular structure of the organic material. This can be easily customized to make a wide range of wavelengths thanks to the endless configurations of organic molecules.
Read more... OLED Fabrication Guide
OLED Fabrication Guide
In this guide, we demonstrate how to make standard OLED devices in a glove box using materials and equipment easily available to any lab. Find out more.
Read more... OLED Testing Guide
OLED Testing Guide
This guide gives you an overview of what to consider when characterising an OLED, as well as tips for their measurement.
Read more...