mCP
CAS Number 550378-78-4
Charge Transport Layer Materials, Fluorescent Host Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Hole Transport Layer Materials, Host Materials, Materials,mCP, often used as a host material for efficient blue phosphorescent LEDs
Increases the photoluminescence internal quantum yield of FIrpic, CAS No. 550378-78-4, mCP, 1,3-Bis(N-carbazolyl)benzene, 1,3-Di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)benzene
1,3-Bis(N-carbazolyl)benzene, known as mCP, with a high triplet energy (ET = 2.91 eV) and a very deep highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) level, is often used as host materials for efficient blue phosphorescent light-emitting diodes. Kawamura et al. demonstrated that the photoluminescence internal quantum yield of the blue emitter of FIrpic could approach nearly 100% when doped into the wide energy gap host of mCP [1].
mCP is one of the most commonly used host materials for fluorescent, phosphorescent, TADF dopants in OLED devices
General Information
| CAS number | 550378-78-4 |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C30H20N2 |
| Molecular weight | 408.49 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 292, 338 nm (in THF) |
| Fluorescence | λem 345, 360 nm (in THF) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.9 eV, LUMO = 2.4 eV |
| Synonyms | mCP, 1,3-Di(9H-carbazol-9-yl)benzene, N,N′-Dicarbazolyl-3,5-benzene |
| Classification / Family | Carbazole derivatives, Host materials, OLEDs, Organic electronics |
Product Details
| Purity |
>99.5% (sublimed) >98.0% (unsublimed) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 173-178 °C (lit.) |
| Appearance | White powder |
*Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals. For more details about sublimation, please refer to the Sublimed Materials for OLED devices page.
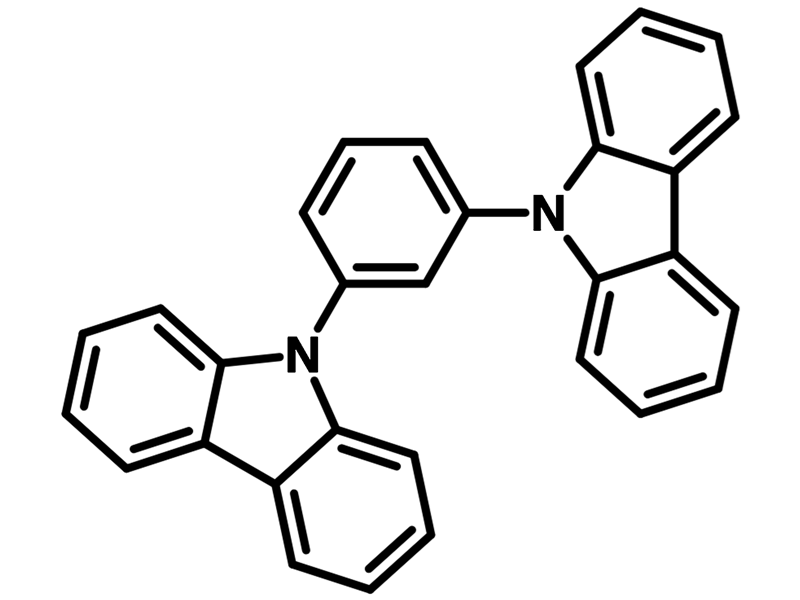
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO(50 nm)/PEDOT:PSS(60 nm)/TAPC(20 nm)/mCP(10 nm)/CbBPCb*(25 nm)/Al(20 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max. EQE | ≥ 30% |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS/NPB/mCP/FPt*(1.5 nm)/OXD-7/CsF/Al [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. EQE | 17.5% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 45 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO(50 nm)/PEDOT:PSS(60 nm)/TAPC(20 nm)/mCP(10 nm)/mCP:BmPyPb*:4CzIPN(25 nm)/TSPO1(35 nm)/LiF(1 nm)/Al(200 nm) [4] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Green |
| Max. EQE | 28.6% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 56.6 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/DNTPD* (60 nm)/NPB (20 nm)/mCP (10 nm)/mCP:FIrpic (25 nm)/CBP:Ir(piq)2acac (5 nm)/BCP (5 nm)/Alq3 (20 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (200 nm) [5] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| EQE@500 cd/m2 | 8.2 % |
| Current Efficiency@500 cd/m2 | 12.7 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (7nm)/NPB (85 nm)/ (PPQ)2Ir(acac):Ir(ppy)3:FIrpic:mCP/TAZ/LiF/Al [6] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. EQE | 20.1% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 41.3 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS(40 nm)/mCP:PVK:OXD-7(33:33:22 wt%):(dfpmpy)2Ir(pic-N-O):(F4PPQ)2Ir(pic-N-O):(EO2- Cz-PhQ)2Ir(acac)*(12:0.25:0.15 wt%)(50-60 nm)/TmPyPB(20 nm)/LiF(1 nm)/Al(150 nm) [7] |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Max. EQE | 11.45% |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 23.04 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 8.04 lm W−1 |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited reference.
When fabricating devices, processing and handling materials in a glove box helps maintain their purity and maintain efficiency by avoiding contamination from particulates, moisture, and airborne impurities.
Pricing
| Grade | Order Code | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sublimed (>99.5%) | M371 | 1 g | £130 |
| Sublimed (>99.5%) | M371 | 5 g | £500 |
| Unsublimed (>98.0%) | M372 | 5 g | £260 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- 100% phosphorescence quantum efficiency of Ir(III) complexes in organic semiconductor films, Y.Kawamura et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 071104 (2005); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1862777.
- Above 30% External Quantum Efficiency in Blue Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Using Pyrido[2,3-b]indole Derivatives as Host Materials, C. Lee et al., Adv. Mater., 25, 5450–5454 (2013).
- Efficient organic light-emitting devices with platinum-complex emissive layer, X. Yang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 98, 033302 (2011); doi: 10.1063/1.3541447.

 mCP MSDS sheet
mCP MSDS sheet