Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) (PVK)
CAS Number 25067-59-8
Hole Transport Layer Materials, Host Materials, Luminosyn™ Polymers, Materials, OFET & OLED Polymer Materials, OLED Materials,Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) (PVK), p-type non-conjugated semiconducting polymer
Hole transport, phosphorescent host and blue emitting layer material
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
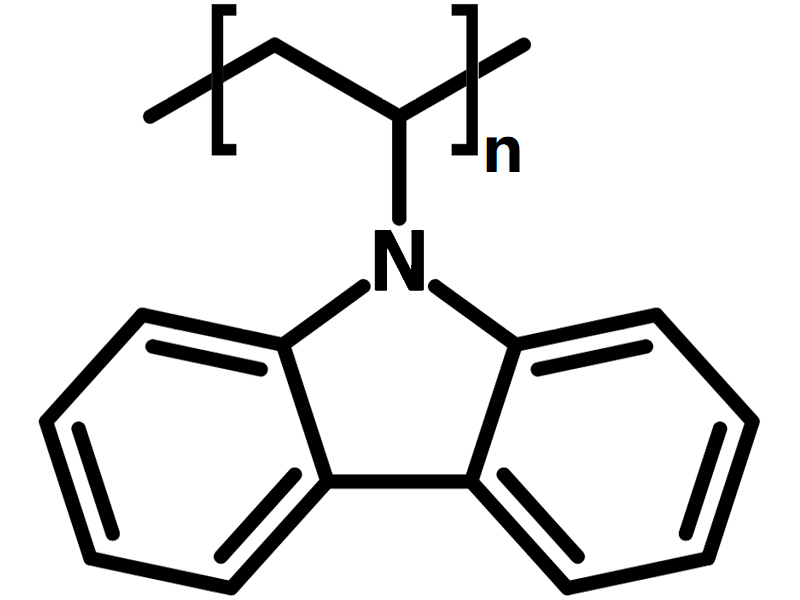
Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) (PVK), CAS number 25067-59-8, consisted by linear chains of repeated molecular units (CH2-CH)n with pendant 9H-carbazole side groups, is a well-known p-type thermoplastic π-conjugated semiconducting polymer with high thermal and chemical stability. It has been widely used as hole-transporting and an electron-blocking layer, host polymer for hole-transporting molecules in OLED to enhance the native hole-transporting properties, and blue PLED emitting layer material. PVK has also been used as photoconductive layers in the xerographic industry and memory devices. PVK, as a non-conjugated polymer, shows unique optical properties and hole transport properties in application of organic electronics due to its hydrophobicity, large hole mobility, solution processability and stability.
It is believed that the electrical conduction in PVK is ruled by both field assisted and temperature activated hopping processes, whereas luminescence occurs via radiative decay of a Frenkel exciton. PVK shows an emission spectrum that covers the entire blue region, owing to the properties of pendent carbazole groups.
PVK can be easily produced in large quantities through controlled radical polymerization of 9-vinylcarbazole. For large quantity, the lead time is 4 – 6 weeks.
General Information
| CAS Number | 25067-59-8 |
| Chemical Formula | (C14H11N)n |
| HOMO / LUMO | HOMO = -5.8 eV, LUMO = -2.2 eV [1] |
| Soluble in | THF, o-xylene, chloroform, chlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene |
| Recommended Processing Solvents at 10mg/ml | Chloroform |
| Full Name | Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) |
| Synonyms | PVK, Poly(n-vinylcarbazole) |
| Classification / Family | Organic semiconducting materials, Large bandgap polymers, Organic photovoltaics, Polymer solar cells, Perovskite solar cells, Hole-transport layer materials, Phosphorescent host materials, OLED |
Batch Details
| Batch | Mw | Mn | PDI | Stock Info |
| M2384A6 | 235,700 | 106,256 | 2.22 | In stock |
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
 Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) - PVK MSDS sheet
Poly(9-vinylcarbazole) - PVK MSDS sheet
Literature and Reviews
- Highly Efficient, Solution-Processed Organic Light Emitting Diodes Based on Thermally Activated Delayed-Fluorescence Emitter with a Mixed Polymer Interlayer, Y. Liu et al., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 1 (2), 543–551 (2018); DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.7b00131.
- Efficient white-light-emitting diodes based on poly(N-vinylcarbazole) doped with blue fluorescent and orange phosphorescent materials, P. Shih et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 251110 (2006);DOI: 10.1063/1.2214141.
-
The effects of polymer molecular weight on the performance of single-layer polymer light emitting diodes, M. Mergani et al., Phys. Scr., T157, 014028 (2013); DOI 10.1088/0031-8949/2013/T157/014028.

