ADN - 9,10-Bis(2-naphthyl)anthracene
CAS Number 122648-99-1
Fluorescent Host Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Host Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Semiconducting MoleculesADN, a promising host material for full colour OLEDs
High thermal and morphological stability. Available online for priority dispatch, 9,10-di(naphth-2-yl)anthracene, 9,10-di(2-naphthyl)anthracene, CAS No. 122648-99-1
9,10-Bis(2-naphthyl)anthracene (ADN), which is well known for its high thermal and morphological stability, is widely used as the host material for blue OLEDs [1, 2].
However, with the development of the co-doping technology, 9,10-Bis(2-naphthyl)anthracene has also shown to be a promising host material for full colour OLEDs due to its wide energy band gap [3, 4, 5].
The co-doping system is a novel technique for colour tuning and increasing the emission characteristics of OLEDs, and the two-step energy transfer in this system plays a very important role in colour tuning and improvement of the device performance.
General Information
| CAS number | 122648-99-1 |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C34H22 |
| Molecular weight | 430.54 g/mol |
| Absorption* | λmax 375,395 nm (in THF) |
| Fluorescence | λem 425 nm (in THF) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.8 eV, LUMO = 2.6 eV |
| Synonyms | ADN 9,10-di(naphth-2-yl)anthracene 9,10-di(2-naphthyl)anthracene |
| Classification / Family | Electron transporting materials, Light emitter layer materials, Fluorescent host materials; Light-emitting diodes, Organic electronics |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Product Details
| Purity | >99.0% (sublimed) >98.0% (unsublimed) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 382-384 °C (lit.) |
| Appearance | White powder |
* Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals, see sublimed materials.
Chemical Structure
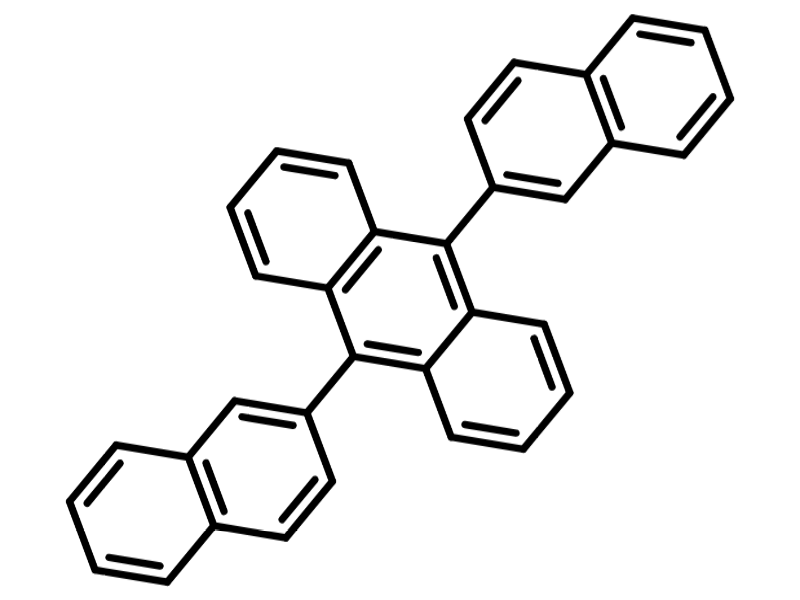
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/NPB (60 nm)/BNA:2 wt% perylene (35 nm)/Alq3(25 nm)/Mg:Ag (200 nm) [6] (BNA is 9,10-Bis(2-naphthyl)anthrace, ADN) |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 4,000 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 1.2 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/NPB (60 nm)/BNA:2 wt% perylene and 0.5 wt% DCJTB* (35 nm)/Alq3 (25 nm)/Mg:Ag (200 nm) [6] (BNA is 9,10-Bis(2-naphthyl)anthrace, ADN) |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. Luminance | 4,100 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 1.65 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO (100 nm)/ NPB (40 nm)/ADN:C6:DCJTB (30 nm)/Alq3(30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Red |
| Max. Luminance | 13, 000 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 4.9 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/NPB (70 nm)/ADN: 0.5% Rubrene (30 nm)/Alq3 (50 nm)/MgAg [7] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. Luminance | 11,700 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 3.7 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 1.72 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO (80 nm)/m-MTDATA (20 nm)/NPB (20 nm)/[ADN:Alq3 (4:1)]:1wt.% DCJTB:0.2wt.%C545T/Alq3 (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [8] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Red |
| Max. Luminance | 11,600 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 3.6 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/ NPB (70 nm)/DPVBi:BCzVBi (15 wt%, 15 nm)/ADN:BCzVBi (15% wt%, 15 nm)/BPhen (30 nm)/ Liq (2 nm)/Al (100 nm) [9] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Deep Blue |
| Max. Luminance | 8,668 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 5.16 cd/A |
*For chemical structure informations please refer to the cited references
Characterisation
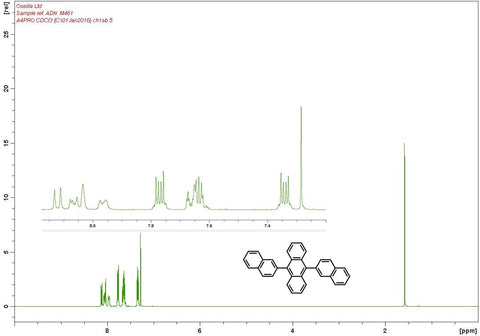
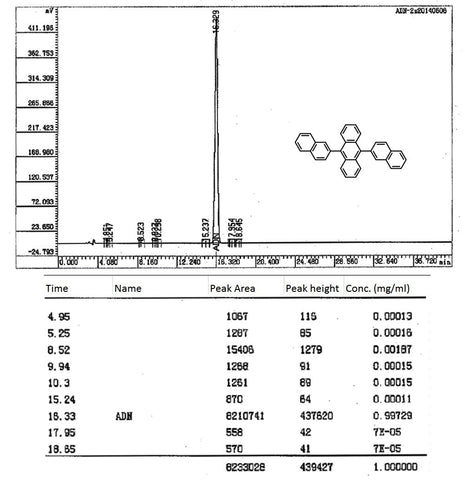
Pricing
| Grade | Order Code | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sublimed (>99.0%) | M461 | 1 g | £290 |
| Sublimed (>99.0%) | M461 | 5 g | £1000 |
| Unsublimed (>98.0%) | M462 | 5 g | £370 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Anthracene derivatives for stable blue-emitting organic electroluminescence devices, J. Shi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3201 (2002); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1475361.
- Study of the Hole and Electron Transport in Amorphous 9,10-Di-(2′-naphthyl)anthracene: The First-Principles Approach, H. Li et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 117 (32), 16336–16342 (2013), DOI: 10.1021/jp4050868
- Highly Efficient and Stable Red Organic Light-Emitting Devices Using 9,10-Di(2-naphthyl)anthracene as the Host Material, H. Tang et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 46 1722 (2007), http://iopscience.iop.org/1347-4065/46/4R/1722.

 ADN MSDS sheet
ADN MSDS sheet