26DCzPPy
CAS Number 1013405-24-7
Host Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Phosphorescent Host Materials, Semiconducting Molecules, TADF Host Materials,26DCzPPy, one of the most popular bipolar host materials used in OLEDs
Sublimed and unsublimed grades are available for 26DCzPPy, 1013405-24-7, 2,6-Bis(3-(carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)pyridine
Combining carbazole electron donors with a high triplet energy and a pyridine electron acceptor with a high electron affinity, 2,6-bis(3-(carbazol-9-yl)phenyl)pyridine (26DCzPPy) is one of the most popular bipolar host materials used in organic light-emitting diodes.
Bipolar host materials are molecules composed of an electron-donating moiety capable of mediating hole injection and transportation, and an electron-withdrawing moiety capable of mediating electron injection and transportation.
General Information
| CAS number | 1013405-24-7 |
|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C41H27N3 |
| Molecular weight | 561.67 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 239, 292 nm (in CH2Cl2) |
| Fluorescence | λem 410 nm (in CH2Cl2) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 6.05 eV, LUMO = 2.56 eV [1] |
| Synonyms |
|
| Classification / Family | Carbazole derivatives, Bipolar charge transport layer materials, Phosphorescent host materials, OLEDs, Organic electronics |
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed grade >99%, Unsublimed grade >99% |
|---|---|
| Melting point | TGA > 370 °C (0.5% weight loss) |
| Appearance | White powder/crystals |
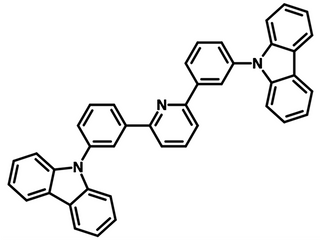
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC (40 nm)/TCTA (2 nm)/26DCzPPy:TCTA:FIrpic (0.4:0.4:0.2) (5 nm)/26DCzPPy:PPT:FIrpic (0.4:0.4:0.2) (5 nm)/3TPYMB (55 nm)/CsF (2 nm)/Al (180 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Power Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 24 lm W−1 |
| Current Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 42 cd/A |
| Power Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 30 lm/W |
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC (40 nm)/TCTA (2 nm)/26DCzPPy:TCTA :FIrpic/26DCzPPy:TCTA:FIrpic:Os/26DCzPPy:PPT:FIrpic:Os/26DCzPPy: PPT:FIrpic/3TPYMB (55 nm)/CsF (2 nm)/Al (180 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Current Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 35.7 cd/A |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT: PSS (60 nm)/26DCzPPy:FIrpic (10 wt.%, 60 nm)/TmPyPB (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max. EQE | 12.1% |
| Max Current Efficiency | 21.8 cd/A |
| Max Power Efficiency | 12.7 lm/W |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT: PSS (60 nm)/TCTA:26DCzPPy:FIrpic (10 wt.%, 60 nm)/TmPyPB (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max. EQE | 14.6% |
| Max Current Efficiency | 25.1 cd/A |
| Max Power Efficiency | 15.7 lm/W |
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC:MoOx (10 nm, 15 wt.%)/TAPC(35 nm)/TcTa:Ir(BT)2(acac) (5 nm, 4 wt.%)/26DCzPPy:FIrpic (5 nm, 15 wt.%)/26DCzPPy:Ir(BT)2(acac) (5 nm, 4 wt.%)/BPhen (40 nm)/Cs2CO3 (1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. EQE | 13.2% |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 35.0 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 30.6 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | Si/SiO2/Al (80 nm)/MoOx: TAPC (43 nm, 15 wt.%)/TAPC (10 nm)/Ir(piq)3:TcTa (3 nm, 6%)/TcTa (2 nm)/FIrpic:26DCzPPy (5 nm, 12 wt.%)/BPhen (2 nm)/PO-01*:26DCzPPy (5 nm, 6 wt.%)/BPhen (40 nm)/Cs2CO3 (1 nm)/Al (2 nm)/Cu (18 nm)/TcTa (60 nm) [4] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| EQE @ 1000 cd/m2 | 10% |
| Current Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 25.6 cd/A |
| Power Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 20.1 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | PEN (120 mm)/ITO (170 nm)/MeO-TPD:F4-TCNQ (100 nm, 4%)/NPB (15 nm)/TCTA (5 nm)/TCTA:Ir(dmppy)2(dpp) (1 nm, 20%)/TCTA:FIrpic (4 nm, 7%)/26DCzPPy:FIrpic (4 nm, 20%)/26DCzPPy:Ir(dmppy)2(dpp) (1 nm, 20%)/TmPyPB (50 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al (200 nm) [5] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 96.8 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 101.3 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO (90 nm)/HATCN (5 nm)/TAPC (65 nm)/10 wt% fac -Ir(mpim)3 –doped TCTA (5 nm)/10 wt% fac -Ir(mpim)3 -doped 26DCzPPy (5 nm)/B3PyPB* (65 nm)/Liq (2 nm)/Al (80 nm) [6] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| EQE @ 100 cd/m2 | 29.6% |
| Current Efficiency @ 100 cd/m2 | 73.2 cd/A |
| Power Efficiency @ 100 cd/m2 | 75.6 lm/W |
| Device structure | ITO/PEDOT:PSS (50 nm)/TCTA (30 nm)/26DCzPPy:Ir(mppy)3 94:6 (40 nm)/TPBI (40 nm)/LiF (0.8 nm)/Al (100 nm) [7] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Green |
| Current Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 41.9 cd/A |
| Power Efficiency @ 1000 cd/m2 | 23.4 lm W−1 |
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC (40 nm)/TcTa (10 nm)/5a* (4%):TcTa (5 nm)/5a* (4%):26DCzPPy (10 nm)/TmPyPB (40 nm)/LiF(1 nm)/Al(100 nm) [8] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Red |
| Max. Luminance | 11,023 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 17.36 cd/A |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 14.73 lm W−1 |
*For chemical structure information please refer to the cited references.
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Blue and white phosphorescent organic light emittingdiode performance improvementbyconfining electrons and holes inside double emitting layers, Y-S.Tsai et al., J. Luminescence 153, 312–316 (2014); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2014.03.040.
- Soluble processed low-voltage and high efficiency blue phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices using small molecule host systems, Y. Doh et al., Org. Electronics, 13, 586–592 (2012); doi:10.1016/j.orgel.2012.01.003.
- Color stable and low driving voltage white organic light-emitting diodes with low efficiency roll-off achieved by selective hole transport buffer layers, Z. Zhang et al., Org. Electronics 13, 2296–2300 (2012); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2012.07.001.
- High performance top-emitting and transparent white organic light-emitting diodes based on Al/Cu/TcTa transparent electrodes for active matrix displays and lighting applications, Z. Zhang et al., Org. Electronics,14, 1452–1457 (2013); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2013.03.007.
- Extremely stable-color flexible white organic lightemitting diodes with efficiency exceeding 100 lmW-1, B. Liu et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2, 9836 (2014); DOI: 10.1039/c4tc01582g.
- Low-Driving-Voltage Blue Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Devices with External Quantum Efficiency of 30%, K. Udagawa et al., Adv. Mater., 26, 5062–5066 (2014); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201401621.
- Interface and thickness tuning for blade coated small-molecule organic light-emitting diodes with high power efficiency, Y-F. Chang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett.,114, 123101 (2013); doi: 10.1063/1.4821881.
-
Efficient red organic electroluminescent devices by doping platinum(II) Schiff base emitter into two host materials with stepwise energy levels, L. Zhou et al., Opt. Lett., 38 (14), 2373-2375 (2013);
http://dx.doi.org/10.1364/OL.38.002373.

 26DCzPPy MSDS sheet
26DCzPPy MSDS sheet