Green Solvents: Why are they the Future?
Whilst efficiencies of lab-scale organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells have continued to rise in recent years, the majority of systems use aromatic halogenated solvents to dissolve the active layer. Whilst these are good for depositing an ideal bulk heterojunction (BHJ) morphology, they often have a negative impact on the environment and human health, and are subject to stricter regulation. This increases the difficulty and cost of fabrication, as well as industrial scalability.1
The most significant advantages of OPVs over other types of new-generation solar cells are the possibility for cheap manufacture and lack of toxic components. In order for this to be fully realised, environmentally-benign solvents must be used. ‘Green’ solvents avoid these issues - the term is typically used to describe non-halogenated solvents, which allow easier management of environmental accumulation - and hence are more favourable for large-scale manufacture.
Issues with using Non-Halogenated Solvents
Finding an appropriate non-halogenated solvent to use as an alternative for an aromatic, halogenated solvent can be difficult. Organic semiconductors are typically made from extended aromatic sub-units, and will thus be most soluble in aromatic solvents. Conversely, environmentally-benign solvents are often non-aromatic and polar, and therefore less likely to be able to dissolve the organic semiconductors.2 Aromatic and non-aromatic solvent alternatives to traditional solvents can be seen in the figure below, where the ideal processing system would be a simple polar solvent (such as water).
Even if solubility is obtained, ideal BHJ morphology may not always follow. The interactions of the solvents and components, as well as the rate of solvent evaporation all have a significant impact on the active layer morphology. Ideally, the solvent needs to facilitate component self-assembly and phase separation, whilst maintaining sufficient solubility to produce a good film.2 Thus, other things must be considered (in addition to solubility) - such as the solvent boiling point, drying behaviour, viscosity and polarity.
Many aspects of morphology are very difficult to control - such as the component orientation, domain purity and temperature-dependant aggregation behaviour. This has led to several OPVs processed from non-halogenated solvents suffering from non-ideal morphology.3 Morphological instability is also important, and different solvents have been shown to impart different stabilities to the same thin film in literature.4
Lastly, the toxicity of the solvent is also vital. Amongst other parameters, this can be assessed using the median lethal dose (or ‘LD50’). This is defined as 'the calculated amount of a substance that can be expected to cause the death of 50% of a defined animal population with a certain amount of time'. It is important to note that being non-halogenated does not always equate to a low toxicity. Some non-halogenated solvents (such as toluene and aniline) can have lower LD50 values, equating to higher toxicity, than those of halogenated solvents (such as chlorobenzene and chloroform). A representation of LD50 for different solvent categories can be seen in the figure below.
It is worth noting that LD50 is not the only measure of toxicity, and may not consider all factors. For example, N-methylpyrollidone (NMP) is an often-mentioned non-halogenated solvent additive with good potential for use in OPVs5 and a high LD50 of 3.9 g/kg2 - but also has severe reproductive toxicity that has led to growing concerns about safety and increased restrictions in other industries.6
Non-Halogenated Solvents in Practice
In current halogenated systems, solvent additives (for example 1,8-diiodooctane (DIO)) are often used alongside the main solvent to improve solubility and morphology. It is generally considered that the high boiling point of DIO slows the annealing process of the active layer, coarsening the phase domains and improving charge transport.7 A similar approach to replacing halogenated solvents can be applied to replace halogenated solvent additives such as DIO. Several non-halogenated alternatives have been identified in literature, such as 1-phenylnaphthalene3 and 1-methylnaphthalene.8 These solvent additives may improve performance simply through low volatility - or in a more complex manner (for example, 1-phenylnaphthalene influences polymer backbone orientation).3
The organic semiconductors themselves can also be altered to improve solubility, for example by adding solubilising substituents, such as alkyl chains. Where components already contain solubilising chains, these can be altered by adding new functional groups (such as tertiary amino groups), or appending new chains to replace the current ones (such as ethylene oxide chains). Any alterations of molecules should be done carefully to maintain current favourable morphology and performance. For example, solubility could be improved by addition of ionic groups such as ammonium, but this has been shown to result in charge traps and charge carrier quenching - hence reducing performance.1
Screening potential solvents can be done beyond simple trial and error, and a key technique used for this are Hansen solubility parameters. Solubility parameters were initially introduced by J. H. Hildebrand in 1936,9 and the Hildebrand solubility parameter was later separated into three separate parameters by Hansen in 1967.10 Here, solvents and solutes are described in terms of dispersive interactions, δD, permanent dipole interactions, δP and hydrogen bonding, δH.11 A variety of halogenated solvents and non-halogenated alternatives can be seen in terms of Hansen solubility parameters (HSPs) in the figure below.11
In order to determine the solubility of a material in a range of solvents, it is tested experimentally in order to approximate the HSPs and a ‘solubility volume’. This is a sphere, the centre being the solute HSPs and the radius a parameter ‘RO’. All solvents inside the sphere dissolve the solvent, and all outside do not. An example of this approach can be seen in the figure below, using HSPs and an RO for P3HT derived from literature.11 The appeal of HSPs is that a number of known solvents can be tested to establish the solute parameters. From this, other potential solvents, solvent additives and solvent mixtures can be identified just from their HSPs, which are readily available in literature.
This approach has been used with success in research.12 For example, there has been work identifying a carbon disulphide/acetone mix as an appropriate alternative to chlorobenzene (based on similar HSP values), where the eventual efficiencies achieved exceeded those of the traditional halogenated solvent.13
The Future of Non-Halogenated Solvent Systems
The greatest success in green solvent systems thus far has been seen with o-xylene,14 trimethylbenzene3 and toluene.15 A summary of published non-halogenated systems can be seen in the figure below.
It is worth noting that for many years, adoption of non-halogenated solvents was restricted by the limited solubility of fullerene derivatives. With the advent of non-fullerene acceptors, the publications of non-halogenated based OPV systems have risen. Non-fullerene acceptors can be chemically modified in the same way that donors are, making solubility easier to achieve through molecular design.1
In addition to combination with non-fullerene acceptors, green solvent systems are also often combined with deposition techniques that have large-scale potential (such as spray coating or blade coating)21 to make the whole system truly scalable. It is likely that these scalable systems will eventually become standard in OPV processing as understanding of morphology is furthered and will be vital for large-scale manufacture moving forward.
Non-fullerene acceptors
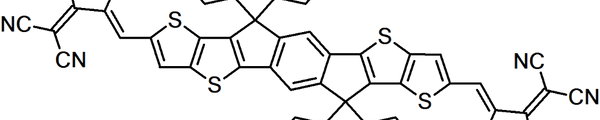
Learn More
When it comes to depositing highly-uniform wet thin films, there are many different solution-processing techniques capable of producing high-quality films at low cost.
Read more... Organic Solar Cells: An Introduction to Organic Photovoltaics
Organic Solar Cells: An Introduction to Organic Photovoltaics
Organic solar cells, also known as photovoltaics (OPVs), have become widely recognized for their many promising qualities. This page introduces the topic of OPVs, how they work and their development.
Read more...References
- Zhang, S., Ye, L., Zhang, H. & Hou, J. Green-solvent-processable organic solar cells. Materials Today (2016). doi:10.1016/j.mattod.2016.02.019.
- McDowell, C. & Bazan, G. C. Organic solar cells processed from green solvents. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry (2017). doi:10.1016/j.cogsc.2017.03.007.
- Zhao, J. et al. Efficient organic solar cells processed from hydrocarbon solvents. Nat. Energy (2016). doi:10.1038/NENERGY.2015.27.