POLED: Plastic or Polymer OLEDs?

pOLED or POLED can refer to different types of organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs). The "p" can stand for "plastic" or "polymer", but these are distinct technologies.
The technology trademarked by LG Display is known as plastic organic light-emitting diodes (pOLED). It involves layering standard OLED materials on a flexible plastic substrate, typically made from materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polyethylene naphthalate (PEN), to produce flexible screens. While "plastic" and "polymer" are sometimes used interchangeably, LG Display specifically uses "plastic" to refer to the OLED base substrate.
Polymer organic light emitting diodes, also referred to as PLEDs, contain light-emitting polymers within their photoactive layer. This is different to most commercial OLED technologies which use small molecules are the photoactive component. Polymer OLEDs are yet to achieve the impressive lifetimes and efficiencies of their small molecule counterparts. However, their solubility and ease of processing puts them at an advantage for scalability and production costs. We may be seeing polymer OLED technology available to buy in the future.
These two distinct technologies leverage polymer materials differently: pOLED refers to the flexible plastic base of devices, while POLED/PLED refers to the use of polymers in the emissive layer of OLEDs.
What is pOLED Technology?
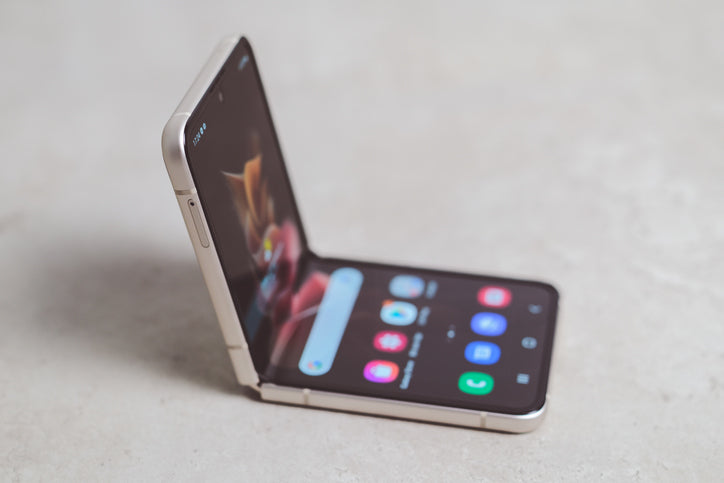

The use of plastic substrates in pOLED displays significantly reduces production costs compared to traditional glass substrates. Plastic materials are easier to manufacture, more lightweight, and less prone to damage during the production process, making them a cost-effective alternative. Additionally, plastic substrates offer enhanced durability with greater resistance to wear and tear, including scratches and cracks. This makes them ideal for devices subject to frequent handling and potential impacts.
This combination of cost-efficiency and durability has made pOLED technology a popular choice for flexible and innovative devices. It is commonly used in foldable smartphones, wearable electronics such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, and other products requiring flexible or curved displays. The flexibility of plastic substrates also allows for unique designs, driving advancements in consumer electronics and expanding the possibilities for new applications.
While pOLED technology continues to evolve and improve, there has previously been issues with burn-in. For example, some owners of Google's Pixel 2 XL reported burn-in after just a few months of use. However, more recent devices using the technology have not experienced the same problem.
What are Polymer OLEDs?

Polymer Organic Light Emitting Diodes (PLEDs) incorporate electroluminescent polymers within their emissive layer. These polymers perform multiple roles typically handled by separate small molecules in conventional OLEDs, including:
- Host Material: Provides a matrix for energy transfer to the emitting species.
- Emitting Material: Responsible for light generation when excited by electrical energy.
- Charge Transport Layer Materials: Facilitates the movement of electrons and holes to the emissive layer for recombination.
For a high-performance PLED, the light-emitting polymer must exhibit several crucial properties:
- High Color Purity: To ensure vibrant and accurate color output.
- Compatibility with Electrode Materials: To maintain device integrity and efficiency.
- High Emission Efficiency: For bright displays with minimal energy consumption.
- High Chemical and Thermal Stability: To extend the device lifespan under various operating conditions.
- High Processibility: To enable ease of fabrication through scalable methods.
The properties of the polymer can be fine-tuned by altering its chemical structure. Modifications such as introducing different chemical groups, substituting atoms, or mixing various monomers can significantly impact characteristics like color, efficiency, and stability. This customization allows for the design of polymers optimized to maximize light emission and other desirable traits.
One of the major advantages of polymer-based OLEDs is their compatibility with cost-efficient fabrication techniques, such as inkjet printing or roll-to-roll processing. These methods not only reduce manufacturing costs but also support the production of flexible and lightweight devices. Consequently, PLEDs hold great potential for making advanced, affordable flexible electronics like smartphones, wearable devices, and large-area displays.
Polymers Used in OLEDs
OLED Materials

Learn More
 OLED Burn-In
OLED Burn-In
As the commercial popularity of OLEDs increased, their advantages over the traditional LED-powered displays became clear.
Read more... What is AMOLED?
What is AMOLED?
The acronym AMOLED stands for active-matrix organic light-emitting diode. It is a type of OLED technology commonly used in large and advanced display systems. The term "active matrix" refers to the arrangement of light-emitting pixels, each controlled by its own dedicated thin-film transistor (TFT) and storage capacitor.
Read more...Contributors
Written by
Application Scientist
Diagrams by
Graphic Designer




