Syringe Pump Flow Rate

The flow rate for a syringe pump refers to the rate at which a fluid is dispensed or withdrawn from a syringe using a syringe pump. It is typically measured in volume per unit of time. Flow rate is controlled by the syringe pump and can be adjusted based on the requirements of the experiment or application.
Syringe pump flow rates are crucial in various research fields, including chemistry, biology, pharmacology, and fluid dynamics, where precise control over fluid delivery or withdrawal is necessary. Precise and accurate control of the flow rate is very important for many of these applications.
Flow rates of Syringe Pumps
Lots of syringe pumps have standard sizes with a standard cross sectional area. Here is a table showing the maximum and minimum achievable flow rate an Ossila syringe pump can achieve for standard syringe sizes.
| Syringe Volume | Syringe Diameter | Minimum Flow Rate | Maximum Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 µl | 0.103 mm | 0.6 pl.s-1 (2.1 nl.hr-1) | 42 nl.s-1 (0.15 ml.hr-1) |
| 10 µl | 0.46 mm | 12.5 pl.s-1 (45 nl.hr-1) | 0.8 µl.s-1 (3 ml.hr-1) |
| 100 µl | 1.46 mm | 0.1 nl.s-1 (0.36 µl.hr-1) | 8.4 µl.s-1 (29.8 ml.hr-1) |
| 1 ml | 4.61 mm | 1.3 nl.s-1 (4.7 µl.hr-1) | 84 µl.s-1 (298 ml.hr-1) |
| 5 ml | 10.3 mm | 6.3 nl.s-1 (22.7 µl.hr-1) | 0.4 ml.s-1 (1.5 l.hr-1) |
| 50 ml | 32.6 mm | 62.6 nl.s-1 (225 µl.hr-1) | 4.2 ml.s-1 (15 l.hr-1) |
Flow Rate Equation
If you know the diameter of your syringe, you can vary the flow rate by changing the linear speed of your syringe pump. This varies according to using the Q=vA formula.
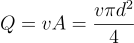
Where Q is flow rate, v is speed of the piston, A is the cross-sectional area of the syringe and d is diameter of the syringe barrel.
The minimum speed of the Ossila Syringe Pump is v=75 nm/s. So for a 1 ml syringe with a diameter d=4.61 mm, the minimum achievable flow rate is Q=1.3 nl.s-1.
Pressure Rates in Syringe Pumps
In the context of syringe pumps, pressure is closely related to flow rate. It is a crucial parameter to consider when operating the pump.
In syringe pumps, there is a direct relationship between pressure and flow rate. The pressure exerted by the pump determines the flow rate by pushing fluid through the system.
Generally, increasing the pressure leads to an increase in flow rate, as long as:
- The syringe pump remains within its operating limits
- The fluid properties remain constant
- The syringe’s pressure capacity (i.e. whether the syringe can withstand this pressure)
However, this relationship may not be linear and could depend on various factors such as the viscosity of the fluid, the diameter and length of tubing, and any restrictions or obstructions in the system.
The pressure capacity of a syringe pump can be influenced by the size and material of the syringe being used. Larger syringes may be able to withstand higher pressures due to their increased volume and structural integrity. Additionally, syringes made from materials with higher tensile strength, such as glass or metal, may have higher pressure tolerances compared to plastic syringes.
You should consider these factors when determining the maximum pressure that a syringe pump can safely handle. Exceeding the pressure limits of a syringe pump can lead to mechanical failure, damage to equipment, or potential hazards to operators.

Can the Ossila Syringe Pump Withstand High Pressure?
The maximum pressure the Ossila syringe pump can exert is 500N. If you exceed the pressure limits of a syringe pump, this can lead to mechanical failure, damage to equipment, or potential hazards to operators.
This makes the Ossila syringe pump is a high-pressure syringe pump. This pump is constructed using durable materials and robust engineering to withstand the forces generated by high-pressure operation.
Despite operating at high pressures, the Ossila syringe pump offers precise control over fluid delivery rates and volumes. This makes the Ossila syringe pump a great tool in applications where precise fluid delivery under elevated pressure is required. These include areas such as chemical synthesis, chromatography, microfluidics and materials science. Overall, the Ossila syringe pump can play a vital role in research applications that demand precise fluid handling under extreme pressure conditions.
Syringe Pump

