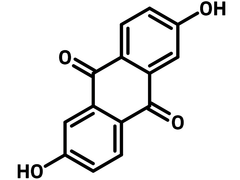
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone
CAS Number 84-60-6
Chemistry Building Blocks, Materials, Monomers, Non-Heterocyclic Building BlocksA widely used anthraquinone building block
Used for the synthesis of semiconducting molecules and polymers in the application of OFETs, OLEDs OPVs, and batteries
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone (CAS number 84-60-6), also known as anthraflavic acid, a plant metabolite, is a 9,10-anthraquinone derivative with the central ring bearing two carbonyl groups being fused to two fully aromatic six-membered rings. It is an isomer of the alizarin dye with a crystal packing as superimposed molecular sheets. Carbonyl dyes has been well known to provide a wide range of colors almost covering the entire visible spectrum, in particular, 9,10-anthraquinone derivatives can give rise to a complete range of shades.
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone is a potent inhibitor of the O-deethylations of ethoxycoumarin and ethoxyresorufin, both catalysed primarily by cytochromes P-448. Anthraflavic acid is a potent inhibitor of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) mutagenicity by virtue of its ability to inhibit both its microsomal and cytosolic activation pathways.
It has also been demonstrated that protons can be reversibly intercalated and deintercalated in crystalline 2,6-dihydroxyanthraquinone (DHAQ) at a potential of −0.21 V in acidic solution with a specific capacity of 110 mAh g-1. The quinone proton battery delivers an equilibrium voltage of 1.1 V, and the capacity retention rate could be as high as 100% after 2600 cycles.
Anthraquinone building block
for the synthesis of APIs and battery materials
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Capped with hydroxyl groups
for facile coupling reactions
High purity
>98% Purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 84-60-6 |
| Chemical Formula | C14H8O4 |
| Full Name | 2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone |
| Molecular Weight | 240.21 g/mol |
| Synonyms | 2,6-DHAQ, 2,6-Dihydroxyanthracene-9,10-dione, Anthraflavic acid, Anthraflavin |
| Classification / Family | Anthraquinone derivatives, Dyes, Semiconductor synthesis intermediates, OLED, OFETs, organic photovoltaics |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | >98% (1H NMR) |
| Melting Point | Tm >320 °C (lit.) |
| Appearance | Yellow/golden powder/crystals |
MSDS Documentation
 2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone MSDS Sheet
2,6-Dihydroxyanthraquinone MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
-
Anthraflavic acid inhibits the mutagenicity of the food mutagen IQ: Mechanism of action, A. Ayrton et al., Mutat. Res. Lett., 207 (3-4); 121-125 (1988); DOI: 10.1016/0165-7992(88)90075-9.
-
Induction of rat hepatic cytochrome P-450 I proteins by the antimutagen anthraflavic acid, A. Ayrton et al., Food Chem. Toxicol., 26 (11-12), 909-915 (1988); DOI: 10.1016/0278-6915(88)90088-9.
-
The Redox-Mediated Nickel–Metal Hydride Flow Battery, T. Páez et al., Adv. Energy Mater., 12 (1), 2102866 (2022); DOI: 10.1002/aenm.202102866.
