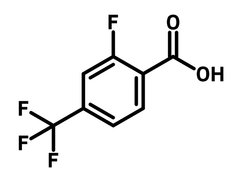
2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid
CAS Number 115029-24-8
Chemistry Building Blocks, Fluorinated Building Blocks, Materials, MonomersA polyfluorinated benzoic acid building block
Used as a precursor for the synthesis of APIs with improved agonistic receptors activity.
Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
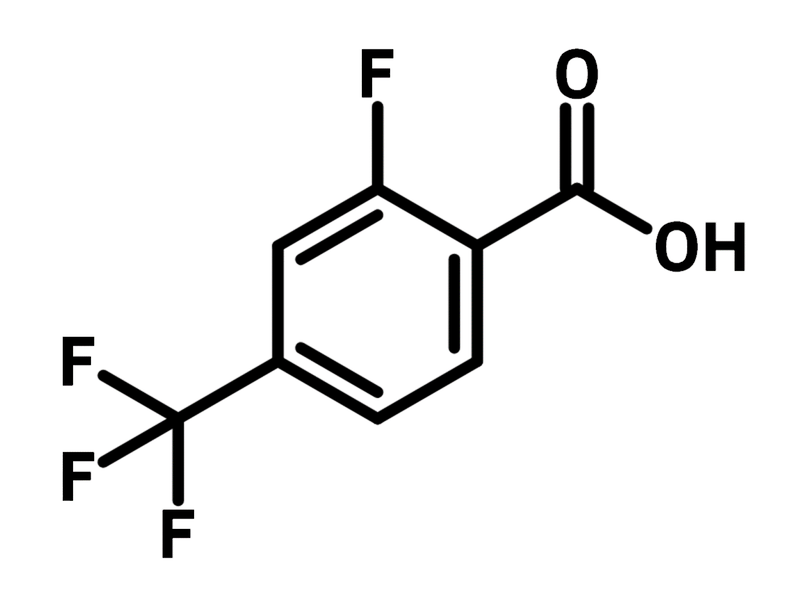
2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid (CAS number 115029-24-8) is a benzoic acid derivative featuring a fluoride and a trifluoromethyl substituents at 2- and 4-positions. As a synthetic building block, 2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid can be easily attached to molecular scaffolds through condensation reactions. A structure-activity relationship study has indicated that the trifluoromethyl and fluoride group introduced by 2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid improve the agonistic activity of G protein-coupled receptors. The increased potency results from the halogen bonding interaction of the fluorinated groups and proteins.
2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid can also undergo functional group exchanges to afford acyl chlorides, aldehydes and anhydrides.
Multiple functional groups
For facile synthesis
Fluorinated benzoic acid building block
for drug discovery, medicinal chemistry and biochemistry research
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
High purity
>98% High purity
General Information
| CAS Number | 115029-24-8 |
| Chemical Formula | C8H4F4O2 |
| Full Name | 2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 208.11 g/mol |
| Synonyms | α,α,α,2-Tetrafluoro-p-toluic acid |
| Classification / Family | Fluorinated building blocks, Benzoic acid building blocks, APIs |
Chemical Structure
Product Details
| Purity | 98% |
| Melting Point | Tm = 168 °C – 170 °C |
| Appearance | White powder |
MSDS Documentation
 2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid MSDS Sheet
2-Fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoic acid MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
- Discovery of novel cccDNA reducers toward the cure of hepatitis B virus infection, D. Chen et al., J. Med. Chem., 65(16), 10938–10955(2022); DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c02215.
- Hydrazones as a privileged structural linker in antitubercular agents: a review, B. Mathew et al., Infect. Disord. Drug Targets, 15, 76–88(2015); DOI: 10.2174/1871526515666150724104411.
- Principles and applications of halogen bonding in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology, R. Wilcken et al., J. Med. Chem., 56, 1363–1388(2013); DOI: 10.1021/jm3012068.