Benzyl Viologen Dichloride
CAS Number 1102-19-8
Charge Transport Layer Materials, Materials, Semiconducting MoleculesElectrochromic Indicator and n-Type Dopant for Semiconductors
For organic and inorganic semiconductors to improve solar cell PCE, BVD, CAS No. 1102-19-8, 1,1'-Dibenzyl-4,4'-bipyridinium Dichloride
Product Information | MSDS | Related Products
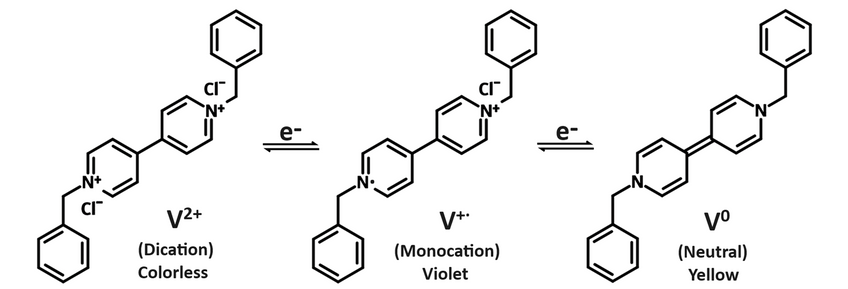
Benzyl viologen dichloride (BVD, CAS number: 1102-19-8) is a bipyridinium dichloride salt with two chlorine anions and positively charged 1,1′-dibenzyl-4,4′-bipyridinium bearing two nitrogen cations. As an electrochromic indicator, benzyl viologen dichloride can go through two-step reduction process to benzyl viologen radical cation (BV+·) and then benzyl viologen neutral (BV0), marked by the distinctive colour changes from colourless to violet purple, and then yellow respectively.
N-type Dopant
For organic and inorganic semiconductors
Worldwide Shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Improved Solar Cell PCE
Enhanced interface compatibility and charge extraction
High Purity
>98% Purity
Benzyl viologen dichloride, together with its both reduced forms of benzyl viologen radical cation (BV+·) and benzyl viologen neutral (BV0), have been used as n-type dopant to promote charge transfer for their strong electron donating properties originated from the viologen unit. Benzyl viologen radical cation (BV+·) doped PNDI(2OD)2T films gained electrical conductivity as high as 1.34 × 10-2 S cm-1 with minimum contact resistance and less than 30% degradation at both 100 °C for 24 h and room temperature for two weeks in a glovebox.
Inverted polymer solar cells based on PTB7-Th:PC71BM as photoactive layer and BVD doped zinc oxide (ZnO) electron transport layer (ETL) showed 16.52% improvement in power conversion efficiency (PCE) while compared to the ones based on pure ZnO. Being a metal oxide inorganic material with hydrophilic properties, ZnO has a general problem of interfacial compatibility with organic active layers of hydrophobic properties at the interface. The doping of ZnO with benzyl viologen not only improves the interface compatibility but also enhances the charge extraction process at the interface.
Benzyl viologen neutral (BV0) has also been used to dope carbon nanotubes, graphene, and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) such as molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) to provide environmentally stable n-type doped semiconducting metallic materials with great charge mobility and device operation stability.
General Information
| CAS Number | 1102-19-8 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C24H22Cl2N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 409.35 g/mol |
| Synonyms | BV-2Cl, BVD, 1,1'-Dibenzyl-4,4'-bipyridinium Dichloride |
| Classification or Family | 4,4′-Bipyridinium salt, n-type dopant, Electron interface, Organic photovoltaics |
Product Details
| Purity | > 98% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point |
260 °C (decomp) (lit.) |
| Appearance | White to light yellow powder/crystals |
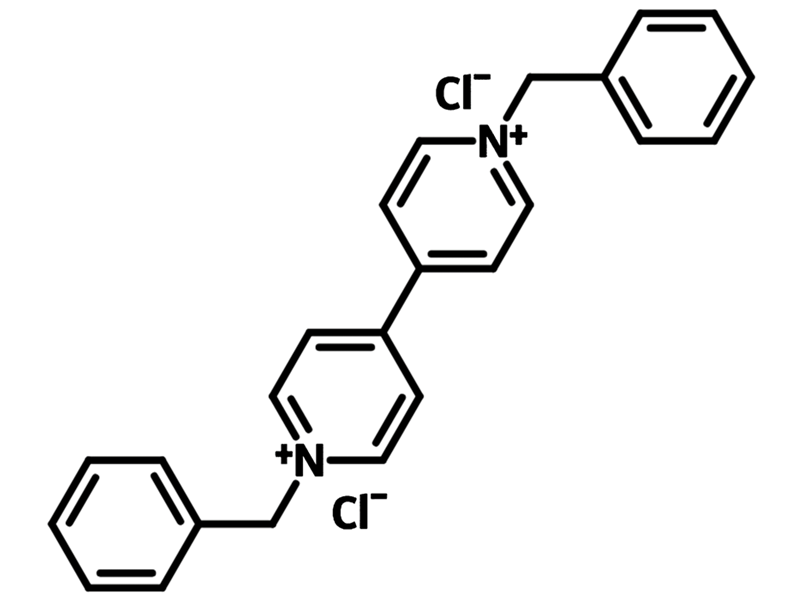
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
 Benzyl viologen dichloride MSDS Sheet
Benzyl viologen dichloride MSDS Sheet
Literature and Reviews
- G. Huseynova et al. (2018); Benzyl viologen as an n-type dopant for organic semiconductors, Org. Electron., 62, 572-580; DOI: 10.1016/j.orgel.2018.06.033.
- T. Tam et al. (2020); The benzyl viologen radical cation: an effective n-dopant for poly(naphthalenediimide-bithiophene), J. Mater. Chem. A, 8, 18916-18924; DOI: 10.1039/D0TA06315K.
- D. Kiriya et al. (2014); Air-Stable Surface Charge Transfer Doping of MoS2 by Benzyl Viologen, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 136 (22), 7853–7856; DOI: 10.1021/ja5033327.


