Molybdenum Diselenide (MoSe2) Crystal
CAS Number 12058-18-3
2D Materials, Low Dimensional Materials, Materials, Molybdenum Diselenide (MoSe2), Transition Metal Chalcogenides (TMCs), Transition Metal Dichalcogenides (TMDs)MoSe2 Crystal, one of the best TMDCs due to large size and high conductivity
High purity (≥99.995%) and available online for fast, secure dispatch
Technical Data | MSDS | Structure | Literature and Reviews | Related Products | Resources and Support
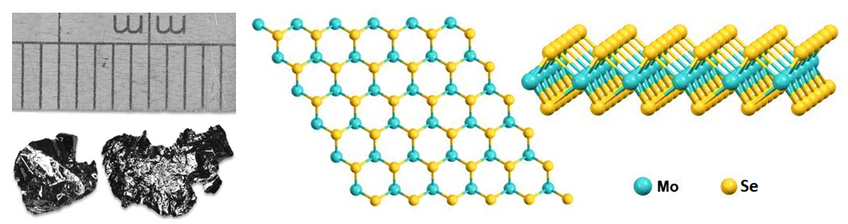
Like most of the transition metal dichalcogenides and graphite, molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), CAS number 12058-18-3, has a two-dimensional layered structure - with the individual layers stacked together by weak van der Waals interactions. Due to the larger size and better conductivity of selenium over sulphur, MoSe2 is one of the best TMDCs of metallic nature. This also provides a great opportunity for hosting counterions in electrochemical energy storage systems (such as lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries).
High Purity
High purity (≥99.995%)
Worldwide shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Low Cost
Low Cost Molybdenum Diselenide
Versatile
Applications in transistors, photo-detectors, and photovoltaics.
Like MoS2, MoSe2 undergoes changes from indirect to direct band-gap transitions when bulk material (such as the bulk crystal) is reduced to monolayer film. However, unlike MoS2, few-layer MoSe2 flakes possess a nearly degenerate indirect and direct band-gap. An increase in temperature/pressure can effectively push the system toward the quasi-2D limit by reducing the coupling between the layers. MoS2, on the other hand, has indirect and direct band-gaps that are well-separated in energy - and hence, far from degenerate.
Compared to MoS2, MoSe2 exhibits higher electrical conductivity.
Technical Data
| CAS Number | 12058-18-3 |
| Chemical Formula | MoSe2 |
| Molecular Weight | 253.86 g/mol |
| Bandgap | 1.41 - 1.58 eV [1] |
| Preparation | Synthetic - Chemical Vapour Transport (CVT) |
| Structure | Hexagonal |
| Electronic Properties | 2D semiconductor |
| Melting Point | >1,300 °C |
| Colour | Black/Dark brown |
| Synonyms | Molybdenum(IV) selenide, Molybdenum selenide |
| Classification / Family | Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), 2D semiconductor Materials, Nano-electronics, Nano-photonics, Electrochemical energy storage system, Materials science |
Product Details
| Form | Purity |
|---|---|
| Crystal | ≥99.995% |
Pricing Table
| Product Code | Form | Size* | Quantity (EA) | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2108A10 | Crystal | Small (≥10 mm2) | 1 | $598 |
| M2108A25 | Crystal | Medium(≥25 mm2) | 1 | $988 |
| M2108A00 | Crystal | Large** (≥100 mm2) | 1 | $2,275 |
*Typical representative size, areas/dimensions may vary
**Item with a lead time of 2 - 3 weeks, please contact us for more information
MSDS Document
Structure of Molybdenum Diselenide Crystal
Literature and Reviews
- Direct observation of the transition from indirect to direct bandgap in atomically thin epitaxial MoSe2, Y. Zhang et al., Nat. Nanotech., 9, 111–115 (2014); DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2013.277.
- Large-Area Synthesis of Monolayer and Few-Layer MoSe2 Films on SiO2 Substrates, X. Lu et al., Nano Lett., 14 (5), 2419–2425 (2014); DOI: 10.1021/nl5000906.
- High-Mobility Transistors Based on Large-Area and Highly Crystalline CVD-Grown MoSe 2 Films on Insulating Substrates, J-S. Rhyee et al., Adv. Mater., 28, 2316–2321 (2016); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201504789.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of 2D materials available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.


 Molybdenum diselenide crystal
Molybdenum diselenide crystal

