n-Butylammonium Iodide
CAS Number 36945-08-1
Materials, Perovskite Materials, Perovskite Precursor MaterialsOverview | Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews | Resources and Support
N-butylammonium iodide (BAI), is commonly added to 3D-perovskite precursor solutions to hinder the growth of 3D-perovskite grains, dramatically decreasing the roughness of films [1].
Compared with methylammonium iodide (MAI), it is believed that ammonium ions with longer chains will not be able to fit at the corner of PbX4's (X = I, Br, Cl) octahedral layers - resulting in the formation of layered perovskite (a.k.a. Ruddlesden–Popper) structures. BAX-incorporated layers demonstrated great improvement on lifetime and operational stability for LED devices.
General Information
| CAS number | 36945-08-1 |
| Chemical formula | C4H12IN |
| Molecular weight | 201.05 g/mol |
| Synonyms | BAI, Butylamine Hydroiodide |
| Classification / Family | Perovskite precursor materials, Perovskite solar cells, Perovskite LEDs |
Product Details
| Purity | 98% |
| Melting point | 173 °C (exp.) |
| Colour | Powder/crystals |
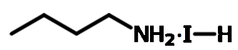
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
 n-Butylammonium iodide MSDS sheet
n-Butylammonium iodide MSDS sheet
Literature and reviews
- Efficient perovskite light-emitting diodes featuring nanometre-sized crystallites, Z. Xiao et al., Nat. Photonics, 11, 108–115 (2017); doi:10.1038/nphoton.2016.269.
- Efficient ambient-air-stable solar cells with 2D–3D heterostructured butylammonium-caesium-formamidinium lead halide perovskites, Z. Wang et al., Nat. Energy, 6 17135 (2017); doi:10.1038/nenergy.2017.135.
- Extremely efficient internal exciton dissociation through edge states in layered 2D perovskites, J.-C. Blancon et al., Science, 10.1126/science.aal4211 (2017); DOI: 10.1126/science.aal4211.
