n-Propylammonium Iodide
CAS Number 14488-45-0
Materials, Perovskite Materials, Perovskite Precursor Materialsn-Propylammonium iodide, additive used to tune properties of perovskite structures
High purity and high quality material available to buy for fast, secure dispatch
Overview | Specifications | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
n-Propylammonium iodide (PAI) is normally used as an additive to perovskite precursor solution to tune the properties of perovskite structures, such as band-gap, stability and electrical conductivity.
By introducing a bulkier organic cation (such as PAI) to the perovskite material with a structure of APbX3, the distance between Pb–I structural units is increased. The longer propyl chain causes the APbX3 perovskite crystal structure to become restricted in dimensions it can propagate along, shifting the crystalline structure from a 3D structure to a 2D structure. The 2D crystalline structures can be used for the fabrication of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), or they can be incorporated into the standard methylammonium framework - which can lead to the formation of 2D-3D hybrid structures - thus improving the stability and electronic properties of grain boundaries within thin films.
General Information
| CAS number | 14488-45-0 |
| Chemical formula | C3H10IN |
| Molecular weight | 187.02 g/mol |
| Synonyms | PAI, Propanamine hydriodide, Propylammonium iodide |
| Classification / Family | Alkylammonium halides, Perovskite precursor materials, Perovskite solar cells, Perovskite LEDs |
Product Details
| Purity | 98% |
| Melting point | 190 °C |
| Colour | Powder/crystals |
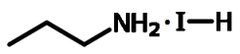
Chemical Structure
MSDS Documentation
 n-Propylammonium iodide MSDS sheet
n-Propylammonium iodide MSDS sheet
Literature and reviews
- Structure and function relationships in alkylammonium lead(II) iodide solar cells, M. Safdari et al., J. Mater. Chem. A, 3, 9201 (2015); DOI: 10.1039/c4ta06174h.
- Efficient ambient-air-stable solar cells with 2D–3D heterostructured butylammonium-caesium-formamidinium lead halide perovskites, Z. Wang et al., Nat. Energy, 6 17135 (2017); doi:10.1038/nenergy.2017.135.
- Extremely efficient internal exciton dissociation through edge states in layered 2D perovskites, J.-C. Blancon et al., Science, 10.1126/science.aal4211 (2017); DOI: 10.1126/science.aal4211.
