TFB
CAS Number 220797-16-0
Hole Injection Layer Materials, Interface Polymers, Materials, Perovskite Interface Materials, Perovskite Materials, Semiconducting PolymersTFB, semiconducting polymer with high mobility
HTL and HIL material for organic electronic devices
Overview | Specifications | MSDS | Pricing and Options | Literature and Reviews
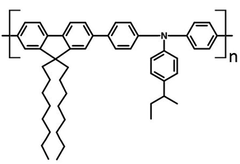
Poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene-alt-N-(4-sec-butylphenyl)-diphenylamine) (TFB), CAS number 220797-16-0, is a triarylamine based semiconductor with a band gap of 3.0 eV (HOMO and LUMO levels of 5.3 eV and 2.3 eV, respectively) and a relatively high hole mobility of 2 ×10-3 cm2 V-1 s-1.
TFB from Ossila was used in the high-impact paper (IF 38.77), Rational molecular passivation for high-performance perovskite light-emitting diodes, W. Xu et al., Nat. Photonics, 13, 418–424 (2019); DOI: 10.1038/s41566-019-0390-x.
Due to its low ionisation potential and high hole mobility, TFB serves primarily as hole transport layer (HTL), hole-injection layer (HIL) and electron-blocking layer (EBL) material in organic electronic devices. When built into device as an interface material, TFB as an electron blocking layer will not only reduce the chance of electron leakage, but also reduce the possibility of exciton quenching between the interface of the active layer and charge transport layer (F8BT/MoOx for example).
General Information
| CAS Number | 220797-16-0 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | (C51H61N)n |
| Absorption* | λmax 390 nm (in THF) |
| Fluorescence | λem 295 nm, 435 nm (in THF) |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.3 eV, LUMO = 2.3 eV |
| Soluble in | THF, toluene, chloroform |
| Recommended Processing Solvents at 10mg/ml | THF (8mg/ml) |
| Synonyms | Poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene-alt-N-(4-sec-butylphenyl)-diphenylamine) |
| Classification / Family | Hole transport material (HTL), Hole injection material (HIL), Electron blocking material (EBL), OLEDs, Perovskite solar cells, Organic and printed electronics |
* Measurable with an optical spectrometer
Product Details
| Melting Point | N/A |
|---|---|
| Colour | Pale yellow powder/fibers |
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device Structure | ITO (120 nm)/PEDOT:PSS(50 nm)/TFB (5 nm)/PYGTPA* (75 nm)/PEGPF* (10 nm)/Ca (10 nm)/Al (100 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Colour |
|
| Max. luminance | 9,242 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 0.85 cd/A |
| Bias | 4.3 V |
| Device Structure | ITO/c-ZnO (50 nm)/F8BT (80 nm)/MoO3 (10 nm)/Au (50 nm) [2] | ITO/c-ZnO (50 nm)/F8BT (80 nm)/TFB (60 nm)/MoO3 (10 nm)/Au (50 nm) [2] |
|---|---|---|
| Colour |
|
|
| Max. luminance | 9,370 cd/m2 | 16,460 cd/m2 |
| Max. Current Efficiency | 0.34 cd/A | 0.93 cd/A |
| Bias | ~0.60 V | ~0.87 V |
| Device Structure | ITO/ZnO/CsPbI3/TFB (60 nm)/MoO3 (5 nm)/Ag (80 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour |
|
| Max. Luminance | 206 cd/m2 |
| Max. EQE | 5.7% |
MSDS Documentation
Pricing
| Batch | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|
| M0981A | 100 mg | £280 |
| M0981A | 250 mg | £560 |
| M0981A | 500 mg | £900 |
Batch details
| Batch Number* | Mw | Mn | PDI | Stock Info |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0981A1 | 42 kDa | 16.8 kDa | 2.5 | Discontinued |
| M0981A2 | 40 kDa | 13.8 kDa | 2.9 | Discontinued |
| M0981A3 | 50 kDa | 30 kDa | 1.65 | In Stock |
*Older batch information available on request.
Literature and Reviews
- All-solution-processed multilayer polymer/dendrimer light emitting diodes, M. Auer-Berger et al., Org. Electronics, 35, 164-170 (2016); http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2016.04.044.
- High Efficiency Composite Metal Oxide-Polymer Electroluminescent Devices: A Morphological and Material Based Investigation, D. Kabra et al., Adv. Mater., 20, 3447–3452 (2008); DOI: 10.1002/adma.200800202.
- Highly Efficient Perovskite Nanocrystal Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by a Universal Crosslinking Method, G. Li et al., adv. Mater., 28, 3528–3534 (2016); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201600064.

 TFB MSDS Sheet
TFB MSDS Sheet