Tin(II) Sulfide (SnS) Crystal
CAS Number 1314-95-0
2D Materials, Low Dimensional Materials, Materials, Post-Transition Metal Chalcogenides (PTMCs), Transition Metal Chalcogenides (TMCs)Tin(II) sulfide crystal, high purity semiconducting material
For applications in next generation photovoltaic solar cells
Technical Data | MSDS | Structure | Literature and Reviews | Related Products | Resources and Support
Tin(II) sulfide (SnS), CAS number 1314-95-0, with a direct energy band-gap of about 1.3 eV, and a high optical absorption coefficient over 5 × 104 cm-1, is a promising new candidate for applications in the next generation of photovoltaic solar cells. Made of earth-abundant, relatively cheap and environmentally-nontoxic elements, SnS is solution processable and stable in both alkaline and acidic conditions.
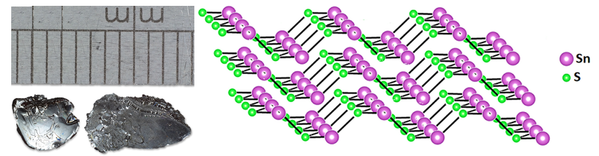
Like the other family members of layered group IV monochalcogenides (including SnSe, GeS, and GeSe), 2D layered SnS has puckered structures - similar to those of black phosphorus. SnS crystallises in the form of an orthorhombic structure, where each Sn(II) atom is coordinated to six S atoms - with three short Sn–S bonds within the surface and three longer Sn-S bonds connecting outer surface of the same layer.
As an analogue to phosphorene, 2D SnS has also been predicted to have strong in-plane anisotropy. However, with two elements of different electronegativity (compared to phosphorene with its single element), the symmetry of SnS structure is rendered, leading to even richer physical properties.
High Purity
≥99.999% Crystal Purity
Worldwide Shipping
Quick and reliable shipping
Semiconductor
2D semiconductor
Applications
Applications in next generation photovoltaic solar cells
Technical Data
| CAS Number | 1314-95-0 |
| Chemical Formula | SnS |
| Molecular Weight | 150.78 g/mol |
| Bandgap | 1.07 - 1.32 eV [1] |
| Preparation | Synthetic - Chemical Vapour Transport (CVT) |
| Structure | Orthorhombic |
| Electronic Properties | 2D semiconductor |
| Melting Point | 882 °C (lit.) |
| Colour | Brown/Yellow |
| Synonyms | Tin sulfide, Stannous sulfide, Tin monosulfide, Tin sulphide, Herzenbergite |
| Classification / Family | Transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), 2D semiconductor materials, Nano-electronics, Nano-photonics, Materials science |
Product Details
| Form | Purity |
|---|---|
| Crystal | ≥99.999% |
Pricing Table
| Product Code | Form | Size* | Quantity (EA) | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2113A10 | Crystal | Small (≥10 mm2) | 1 | £520 |
| M2113A25 | Crystal | Medium (≥25 mm2) | 1 | £850 |
*Typical representative size, areas/dimensions may vary
Shipping is free for qualifying orders.
MSDS Documents
Structure of Tin(II) Sulfide Crystal
Literature and Reviews
- Band-structure, optical properties, and defect physics of the photovoltaic semiconductor SnS, J. Vidal et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 032104 (2012); DIO: 10.1063/1.3675880.
- Few-Layer Tin Sulfide: A New Black-Phosphorus-Analogue 2D Material with a Sizeable Band Gap, Odd−Even Quantum Confinement Effect, and High Carrier Mobility, C. Xin et al., J. Phys. Chem. C, 120, 22663−22669 (2016); DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b06673.
- Growth of Large-Size SnS Thin Crystals Driven by Oriented Attachment and Applications to Gas Sensors and Photodetectors, J. Wang et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 8, 9545−9551 (2016); DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b01485.
Related Products
We stock a wide range of 2D materials available to purchase online. Please contact us if you cannot find what you are looking for.

 Tin(II) sulfide crystal
Tin(II) sulfide crystal

