DMAC-DPS
CAS Number 1477512-32-5
Blue Dopant Materials, Dopant Materials, High Purity Sublimed Materials, Materials, OLED Materials, Semiconducting Molecules,DMAC-DPS, blue dopant material in TADF-OLED devices
Bipolar charge-transporting capability and high (PLQYs), 10,10′-(4,4′-Sulfonylbis(4,1-phenylene))bis(9,9-dimethyl-9,10-dihydroacridine, CAS No. 1477512-32-5, Sublimed ≥99.0%
DMAC-DPS is great for applications in TADF-OLED devices, thanks to its rather broad blue emission nature with a full width at half-maximum of ≈ 80 nm, short lived excited-state (≈3.0 µs in solid films), bipolar charge-transporting capability, and high photoluminescence quantum yields (PLQYs).
PLQYs of blue-emitting DMAC–DPS can be increased from 0.80 to 0.90 by changing the host from mCP to bis(2-(diphenylphosphino)phenyl)ether oxide (DPEPO).
DMAC-DPS is normally used as a blue dopant material in TADF-OLED devices.
General Information
| CAS number | 1477512-32-5 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 10,10′-(4,4′-Sulfonylbis(4,1-phenylene))bis(9,9-dimethyl-9,10-dihydroacridine |
| Chemical formula | C42H36N2O2S |
| Molecular weight | 632.81 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 286 nm in Toluene |
| PL | λem 469 nm in Toluene |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.92 eV, LUMO = 2.92 eV; T1=2.91 eV[1] |
| Synonyms | DMAC-DPS |
| Classification / Family | Acridine derivatives, Blue emitter, TADF blue host materials, Phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices (PHOLEDs), Sublimed materials |
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed >99.0% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | > 250 °C (0.5% weight loss) |
| Appearance | Pale yellow powder/crystals |
*Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals. For more details about sublimation, please refer to the Sublimed Materials.
Chemical Structure
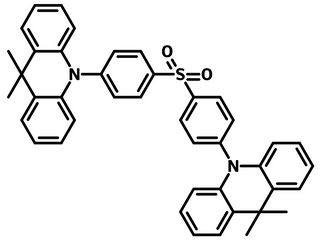
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/HATCN (7 nm)/ TAPC (40 nm)/DCDPA (10 nm)/ CzCbPy: 20 wt% DMAC-DPS (25 nm)/TSPO1 (5 nm)/TPBi (30 nm)/LiF (1.5 nm)/Al (100 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max Current Efficiency | 35.0 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 22.9% |
| Max. Luminance | 8, 035 cd/m2 |
| Device structure | ITO/a-NPD (30 nm)/TCTA (20 nm)/CzSi (10 nm)/DMAC–DPS:DPEPO (20 nm)/DPEPO (10 nm)/TPBI (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max EQE | 19.5% |
| Device structure | ITO (180 nm)/ HATCN (10 nm)/ TCTA: 20% HATCN (50 nm)/TCTA (20 nm)/mCP (10 nm)/DMAC-DPS (20 nm)/DPEPO (10 nm)/ BmPyPB:3% Li2CO3 (35 nm)/ Li2CO3(1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max Current Efficiency | 32.3 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 16.6% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 32.8 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO (180 nm)/ HATCN (10 nm)/ TCTA: 20% HATCN (50 nm)/TCTA (20 nm)/mCP (10 nm)/DPEPO:10% DMAC-DPS (20 nm)/DPEPO (10 nm)/ BmPyPB:3% Li2CO3 (35 nm)/ Li2CO3(1 nm)/Al (100 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max Current Efficiency | 40.3 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 20.7% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 34.3 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (6 nm)/NPB (70 nm)/mCP (5 nm)/DPDPO2A*:DMAC-DPS (10% wt 20 nm)/DPDPO2A* (5 nm)/BPhen (30 nm)/LiF (1 nm)/Al [4] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Blue |
| Max Current Efficiency | 42.1 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 22.5% |
| Max Luminescence | 14,626 cd/m2 |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 52.9 lm W-1 |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited references.
When fabricating devices, processing and handling materials in a glove box helps maintain their purity and maintain efficiency by avoiding contamination from particulates, moisture, and airborne impurities.
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- Multi-carbazole encapsulation as a simple strategy for the construction of solution-processed, non-doped thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters, J. Luo et al., J. Mater. Chem. C, 4, 2442-2446 (2016); DOI: 10.1039/C6TC00418K.
- Efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes employing thermally activated delayed fluorescence, Q. Zhang et al., Nat. Photonics, 8, 326–332 (2014); DOI: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.12.
- High-Performance Hybrid White Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Superior Effi ciency/Color Rendering Index/Color Stability and Low Efficiency Roll-Off Based on a Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Emitter, Z. Wu et al., Adv. Funct. Mater., 26, 3306–3313 (2016); DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201505602.

 DMAC-DPS MSDS sheet
DMAC-DPS MSDS sheet