TTPA, an green dopant material in TADF devices
Available online in sensible quantities for priority dispatch
Specifications | Pricing and Options | MSDS | Literature and Reviews
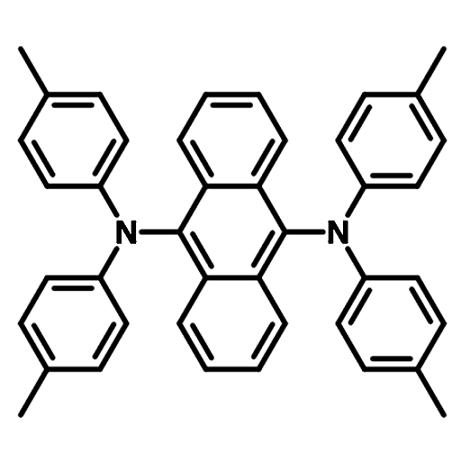
9,10-Bis[N,N-di-(p-tolyl)-amino]anthracene, TTPA, is commonly used as a green dopant material in TADF-OLED devices.
Bearing two triarylamine units, TTPA is also electron-rich in nature. It can be used as a hole-transporting material for OLED, OPV, and perovskite solar cell applications.
General Information
| CAS number | 177799-16-5 |
|---|---|
| Full name | 9,10-Bis[N,N-di-(p-tolyl)-amino]anthracene |
| Chemical formula | C42H36N2 |
| Molecular weight | 568.75 g/mol |
| Absorption | λmax 294, 471 nm in DCM |
| Fluorescence | λem 554 nm in DCM |
| HOMO/LUMO | HOMO = 5.5 eV, LUMO = 3.1 eV [1] |
| Synonyms | TTP1; ATTP |
| Classification / Family | Triarylamine derivatives, Organic electronics, Hole transport layer materials (HTL), Electron-blocking layer materials (EBL), TADF green dopant materials, TADF-OLEDs, Sublimed materials. |
Product Details
| Purity | Sublimed: >99.0% (HPLC) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | TGA: >280 °C (0.5% weight loss) |
| Appearance | Yellow powder/crystals |
*Sublimation is a technique used to obtain ultra pure-grade chemicals. For more details about sublimation, please refer to the Sublimed Materials.
Chemical Structure
Device Structure(s)
| Device structure | ITO/α-NPD (30 nm)/DPEPO (10 nm)/TPBi (40 nm)/1 wt% DBP:10 wt% TTPA:mCP (8 nm)/mCP (2 nm)/DMAC-DPS (7.5 nm)/LiF (0.5 nm)/Al (100 nm) [1] |
|---|---|
| Colour | White |
| Max. EQE | 12.1% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 22 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/TAPC (35 nm)/1 wt%-TTPA:50 wt%-ACRXTN:mCP (15 nm)/TPBi (65 nm)/LiF (0.8 nm)/Al (100 nm) [2] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Green |
| Max Current Efficiency | 45 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 15.8% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 47 lm W-1 |
| Device structure | ITO/MoO3 (2 nm)/TAPC (40 nm)/TCTA (10 nm)/CzSi (3 nm)/CzSi:Pd-B-1* (10%):TTPA (1%) (20 nm)/TSPO1 (10 nm)/TmPyPb (40 nm)/LiF (1.2 nm)/Al (150 nm) [3] |
|---|---|
| Colour | Green |
| Max Current Efficiency | 38.85 cd/A |
| Max EQE | 10.41% |
| Max. Power Efficiency | 38.14 lm W-1 |
*For chemical structure information, please refer to the cited references.
Pricing
| Grade | Order Code | Quantity | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2129A1 | 250 mg | £250 |
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2129A1 | 500 mg | £420 |
| Sublimed (>99% purity) | M2129A1 | 1 g | £680 |
MSDS Documentation
Literature and Reviews
- High-Efficiency White Organic Light-Emitting Diodes Based on a Blue Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Emitter Combined with Green and Red Fluorescent Emitters, T. Higuchi et al., Adv. Mater., 27, 2019–2023 (2015); DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404967.
- High-efficiency organic light-emitting diodes with fluorescent emitters, H. Nakanotani et al., Nat. commun., 5:4016 (2014); DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5016
- Highly luminescent palladium(II) complexes with sub-millisecond blue to green phosphorescent excited states. Photocatalysis and highly efficient PSF-OLEDs, P-K. Chow et al., Chem. Sci., 7, 6083-6098 (2016); DOI: 10.1039/C6SC00462H.

 TTPA MSDS sheet
TTPA MSDS sheet