Semiconducting Molecules
Semiconducting molecules are organic compounds which exhibit semiconducting properties. Semiconducting molecules are composed of carbon-based organic compounds, unlike traditional semiconductors like silicon which are inorganic materials.
Semiconducting molecules include hole and electron transport layer, host, and first generation fluorescent, second generation phosphorescent, third generation thermally activated delayed fluorescent (TADF) and fourth generation multi-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescent (MR-TADF) materials in application of organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs), organic field-effect transistors (OFETs) and photovoltaic devices.
Features and Properties
- Tuneable conductivity. Semiconducting molecules can conduct electricity. Their properties can be tuned by modify the chemical structure, allowing precise control over their conductivity.
- Low cost-manufacturing. Low cost, solution-based processing methods can be used leading to reduced device manufacturing costs. Semiconducting molecules are also generally cheaper to produce than inorganic semiconductors.
- Flexibility. Organic molecules are more flexible than inorganic materials, enabling the fabrication of flexible or stretchable devices.
Explore our small-molecule semiconductors for use as emitters and interlayers in TADF-based OLEDs, active materials in OFETs, and as interface materials to perovskites. Maximize your device efficiency by fabricating and testing new devices in a glove box environment.
Jump to: Semiconducting Molecules by Role | Browse all Semiconducting Molecules | Resources and Support
Semiconducting Molecules by Role
Browse Semiconducting Molecules
Related categories: Transport layer materials, Dopant materials, Host materials, TADF materials
Filter by purification technique:
Page 1 of 2

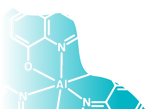
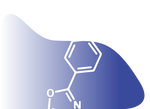








































































































![4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-[4-(triphenylvinyl)phenyl]-1,3,2-dioxaborolane CAS 1260865-91-5](http://www.ossila.com/cdn/shop/files/tep-bpin-chemical-structure-title.png?v=1721213362&width=190)